New Paper : "Biomimetic aerogels with hierarchical honeycomb architecture for superior CO2 adsorption, selectivity, and structural integrity" In:Nature Communications Materials. doi: 10.1038/s43246-02
- trifkovicgroup
- Jul 25, 2025
- 1 min read
Updated: Sep 29, 2025
Sucharita Pal, Edward PL Roberts, Milana Trifkovic & Giovanniantonio Natale
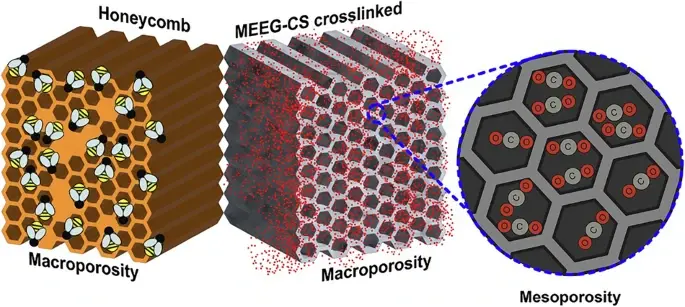
In structured adsorbents, achieving mesoporosity, crucial for efficient gas adosorption, is challenging, which restricts mass transport and accessibility to active sites. Here, we address this limitation by developing the first hierarchically porous honeycomb aerogels that replicate hexagonal pores at both the macro-level and micro-level wall structure. This design, inspired by nature’s most efficient patterns, enables us to achieve CO₂ adsorption capacity (3.94 mmol g−¹ at 298 K and 1 bar), selectivity (65.2 CO₂/N₂), and high specific surface area (370 m² g−¹). The honeycomb aerogels are constructed from manganese dioxide (MnO₂) functionalized electrochemically exfoliated graphene (MEEG) and chitosan (CS). By optimizing the MnO₂ loading and the MEEG to CS weight ratio, we achieved dual-scale hexagonal porosity, enabling a hybrid physical and chemical adsorption mechanism. The hybrid adsorption leverages the rapid kinetics of chemisorption and ease of regeneration characteristic of physisorption, making these materials highly efficient. This highlights the synergy between enhanced surface accessibility of primary amine groups and selective adsorption properties, setting a new standard for hierarchically structured materials.